DMI – Graduate Course in Computer Science
Copyleft
![]() 2016-2017 Giuseppe Scollo
2016-2017 Giuseppe Scollo
this tutorial deals with:
program development for dedicated systems often takes place on machines that are based on a different processor than the target one, viz. that which is meant for their execution
the cross-compilers and utilities here considered are GNU free software, that typically have names <target>–gcc for the compiler, where <target> indicates the target architecture, and <target>–<util> for the utility <util>, such as for example
the use of the nios2-elf-gcc cross-compiler and of a couple of binary utilities, exposed in sect. 7.4 of (Schaumont 2012) for the example in Listing 7.7, can be reproduced by running the scripts provided in the nios2binutils_example.tgz archive, available in the crosstools folder of the reserved lab area
for each version, two scripts are available:
the example showcases the use of the simulator SimIt-ARM v. 2.1 both for the analysis of the executable and for the command-line simulation of a program for GCD computation with Euclid's algorithm (Listing 7.11 in (Schaumont, 2012))
compilation goes through the cross-compiler arm-linux-gcc, for ISA ARMv5, implemented in the StrongARM processor among others
archive arm_simitarm_example.tgz, available in folder crosstools of the reserved lab area, provides two scripts for this tutorial:
the example deals with the execution, on an ARM Cortex-A9 in the Altera DE1-SoC system, of a variation of the program in Listing 7.1, where the main() function body is replaced by
loading and execution take place by means of the program altera-monitor-program, under control of its included GDB debugger and through the JTAG connection between the program and the DE1-SoC
the archive arm_cortex-a9_example.tgz, available in the crosstools folder of the reserved lab area contains the following scripts:
the same C source from the previous example may be compiled and executed by a NIOS II softcore on the FPGA of the DE1-SoC system, in this example with no other script, just to explore the use of the debugger included in the monitor program
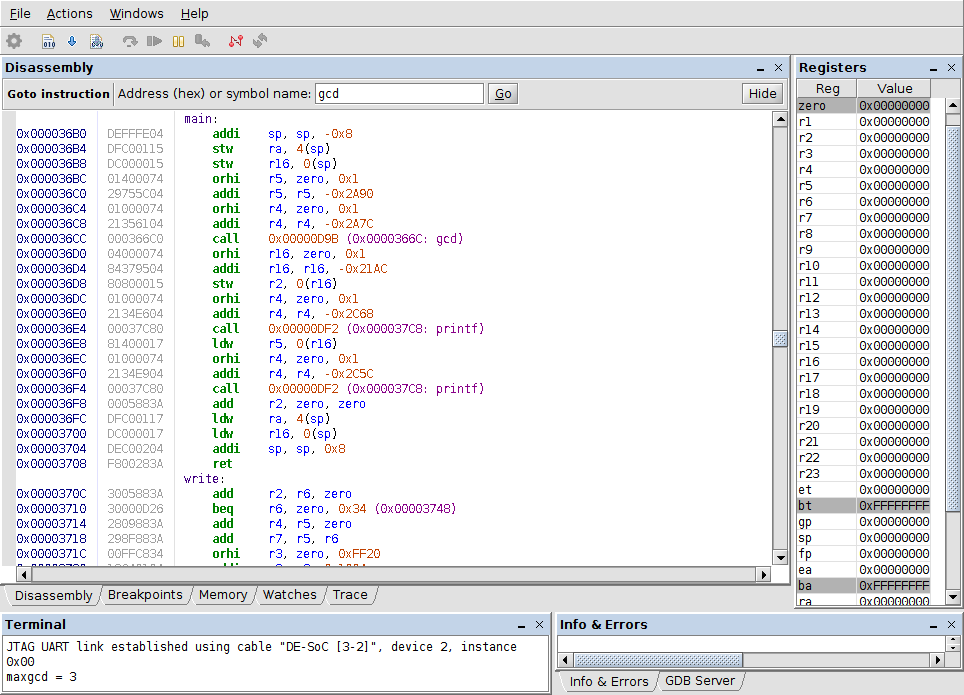
a snapshot of execution on an Altera DE1-SoC board, controlled by the Altera Monitor Program debugger
run the scripts provided with this tutorial, examine the files produced by their execution, find a few not well-known aspects of their contents, search the web for information about them and produce some tutorial documentation in form of a list of questions and answers
here are three examples of question and answer, one for each of the three types described above:
recommended readings:
readings for further consultation:
useful materials for the proposed lab experience: