DMI – Graduate Course in Computer Science
Copyleft
![]() 2016-2017 Giuseppe Scollo
2016-2017 Giuseppe Scollo
Motivation and fundamental concepts of:
A "traditional" definition:
A "nontraditional" definition:
What's the difference?
Why the difference? See next...
Hardware flexibility, to various extent:
The two terms are not synonyms:
Embedded systems: wide variety, fast-growing markets:
Dedicated systems are also components or subsystems of general-purpose information processing systems:
Technological factors tip the balance in favour of more hardware:
| Energy efficiency of AES encryption implementations | |||||
| Gb/J: | 10-6 | 10-3 | 10-2 | 100 | 101 |
| platform: | Java KVM Sparc | C Sparc | Asm Pentium-III | Virtex-II FPGA | 0.18μm CMOS ASIC |
Best-match for HW/SW codesign: parallel computing platforms
Economical factors tip the balance in favour of more software:
The structured collection of all possible implementations of a given application
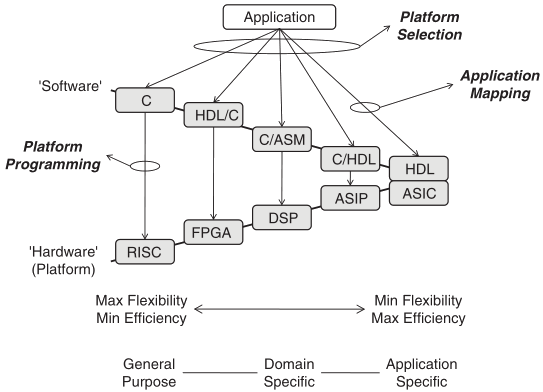
Schaumont, Fig. 1.7 - The hardware-software codesign space
Definable by the time granularity of elementary (atomic) actions
Starting at the lowest abstraction level:
Feature constructs for specification of (static) structure as well as of (dynamic) behaviour
The three most prominent ones, all with discrete event semantics:
A more concise language, for RTL description of synchronous hardware:
Collatz trajectories
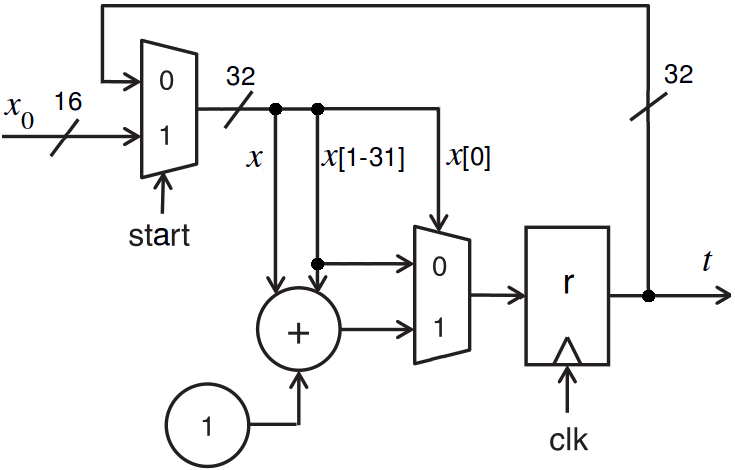
dp collatz (
in start : ns(1) ;
in x0 : ns(16) ;
out t ns(32)) {
reg r : ns(32) ;
sig x : ns(32) ;
always {
t = r ;
x = start ? x0 : r ;
r = x[0] ? x + (x >> 1) + 1 : x >> 1 ;
}
}
A generic SoC design template:
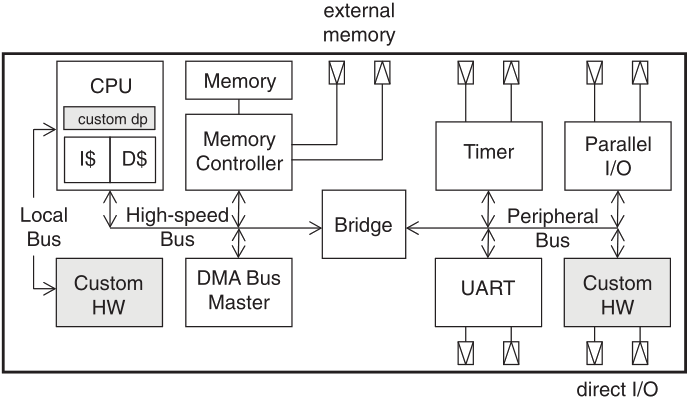
Schaumont, Fig. 8.1 - Generic template for a system-on-chip
Basic concepts:
Collections of HW and SW tools for codesign development and testing
FPGA development boards are the basic hardware tools to this purpose
they come equipped with sophisticated software systems for high-level codesign and cosimulation
for example, the DE1-SoC development board by Altera (see picture), which hosts a Cyclone V FPGA chip, with an ARM Cortex-A9 processor on the same chip, may include two NIOS II softcore processors on the FPGA, and is supported by the Quartus Prime Lite software, freely available
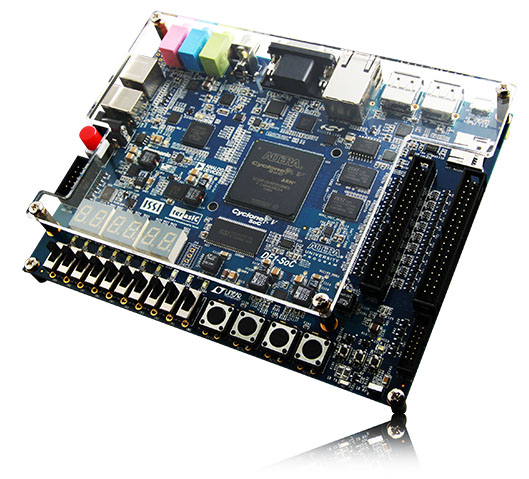
Altera DE1-SoC development board with Cyclone V FPGA
source: Altera University Program
Open-hardware platforms include: Parallella, Arduino, Cosino ...
Cosimulation may also be carried out on a software platform, with no FPGA involved
such a platform typically includes:
cycle-accurate cosimulation allows designers to estimate the performance of codesign solutions well before their actual implementation
A collection of Debian packages for Ubuntu installation (updated for every new LTS)
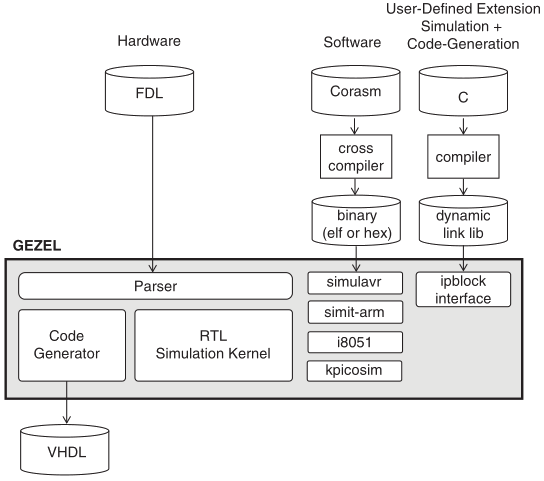
Schaumont, Fig. A.1 - Overview of the GEZEL tools
P.R. Schaumont:
A Practical Introduction to Hardware/Software Codesign
2nd Edition, Springer (2012)
P. Wilson
Design Recipes for FPGAs: Using Verilog and VHDL
2nd Edition. Newnes, Elsevier (2015)
P. Marwedel:
Embedded System Design:
Embedded Systems Foundations of Cyber-Physical Systems
2nd Edition. Springer (2011)
F. Vahid & T. Givargis:
Embedded System Design: A Unified Hardware/Software Introduction
Wiley (2002)
C. Brandolese, W. Fornaciari:
Sistemi embedded: sviluppo hardware e software per sistemi dedicati
Pearson, Milano (2007)
E.A. Lee & S.A. Seshia:
Introduction to Embedded Systems - A Cyber-Physical Systems Approach
2nd Edition, Version 2.0 (2015)
F. Vahid, T. Givargis & B. Miller:
Programming Embedded Systems: An Introduction to Time-Oriented Programming
Version 4.0. Uniworld (2012)
M. Wolf:
Computers as components:
Principles of embedded computing system design
3rd Edition, Morgan Kaufmann (2012)
D. Ibrahim
PIC Microcontroller Projects in C
2nd Edition. Newnes, Elsevier (2014)
Hardware/Software Codesign,
Patrick Schaumont, VirginiaTech
www.faculty.ece.vt.edu/schaum/teaching/4530
Hardware/Software Codesign with FPGAs, Jim Plusquellic,
U. of New Mexico
ece-research.unm.edu/jimp/codesign
Cyber-physical system fundamentals,
P. Marwedel, TU Dortmund
ls12-www.cs.tu-dortmund.de/daes/en/lehre/courses/sommersemester-2015/ss15-cyber-physical-system-fundamentals/slides-cpsf-ss-2015.html
Introduction to Embedded Systems,
Edward A. Lee and Sanjit A. Seshia, U. of Berkeley
chess.eecs.berkeley.edu/eecs149
Free online course on Embedded Systems,
EE Herald, Bangalore
eeherald.com/section/design-guide/esmod.html
GEZEL: rijndael.ece.vt.edu/gezel2
Altera (University Program): www.altera.com/support/training/university/overview.html
Xilinx: www.xilinx.com
CUDA: developer.nvidia.com/cuda-zone
Parallella: www.parallella.org
Arduino: www.arduino.cc
Cosino: www.cosino.io